Absence results in no immune response, a fundamental principle in immunology. The immune system, our body’s defense mechanism, relies on antigens to trigger a response against foreign invaders. Without antigens, the immune system remains inactive, leading to severe consequences.
This article delves into the mechanisms of immune response, the significance of antigens, and the implications of impaired immune function. We explore clinical applications, current research, and future directions in understanding the absence of immune response.
Immune Response Mechanisms
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against foreign substances, known as antigens. These antigens can include bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and toxins. The immune system recognizes and responds to these antigens by mounting an immune response, which is a series of coordinated actions that eliminate the foreign invaders and protect the body from infection and disease.
There are two main types of immune responses: innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense against infection. It is made up of physical barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, as well as chemical barriers, such as stomach acid and saliva.
Innate immunity also includes cells that can recognize and destroy foreign invaders, such as neutrophils and macrophages.
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity is the body’s second line of defense against infection. It is made up of cells that can recognize and destroy specific antigens. Adaptive immunity is also responsible for immunological memory, which allows the body to mount a faster and more effective response to a foreign invader that it has encountered before.
Absence of Antigens
Antigens are molecules that are recognized by the immune system as foreign or potentially harmful. They trigger an immune response, which is the body’s way of defending itself against infection and disease. Antigens can be found on the surface of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, as well as on the surface of cells that have been damaged or infected.The
absence of antigens in the body can have several consequences. First, it can lead to immunosuppression, which is a weakened immune system. Immunosuppression can make the body more susceptible to infection and disease. Second, the absence of antigens can prevent the immune system from recognizing and attacking cancerous cells.
This can allow cancer cells to grow and spread unchecked.There are a number of factors that can lead to the absence of antigens in the body. One factor is malnutrition. Malnutrition can lead to a deficiency of nutrients that are necessary for the production of antibodies and other immune cells.
Another factor is certain medical conditions, such as HIV/AIDS and leukemia, which can damage the immune system and make it less able to produce antibodies and other immune cells.The absence of antigens in the body is a serious problem that can have a number of negative consequences.
It is important to be aware of the factors that can lead to the absence of antigens and to take steps to prevent them.
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a condition in which the immune system is weakened. This can be caused by a number of factors, including:* Malnutrition
- Certain medical conditions, such as HIV/AIDS and leukemia
- Medications that are used to suppress the immune system, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs
Immunosuppression can make the body more susceptible to infection and disease. It can also prevent the immune system from recognizing and attacking cancerous cells. This can allow cancer cells to grow and spread unchecked.There are a number of ways to prevent immunosuppression.
These include:* Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Avoiding tobacco smoke and alcohol
- Getting vaccinated
- Taking medications as directed by your doctor
If you have any concerns about your immune system, it is important to talk to your doctor.
Impaired Immune Function
The absence of an immune response can lead to impaired immune function, leaving individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases. Without a proper immune response, the body is unable to recognize and combat foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
This can result in increased susceptibility to infections and a higher risk of developing severe illnesses.
Examples of Conditions and Diseases Resulting from Impaired Immune Function
Impaired immune function can lead to a range of conditions and diseases, including:
- Immunodeficiency disorders, such as Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), which are characterized by a weakened or absent immune system.
- Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, leading to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
- Allergies, which are exaggerated immune responses to harmless substances, such as pollen or dust.
- Chronic infections, where the immune system fails to clear an infection, leading to persistent symptoms and potential complications.
Clinical Implications
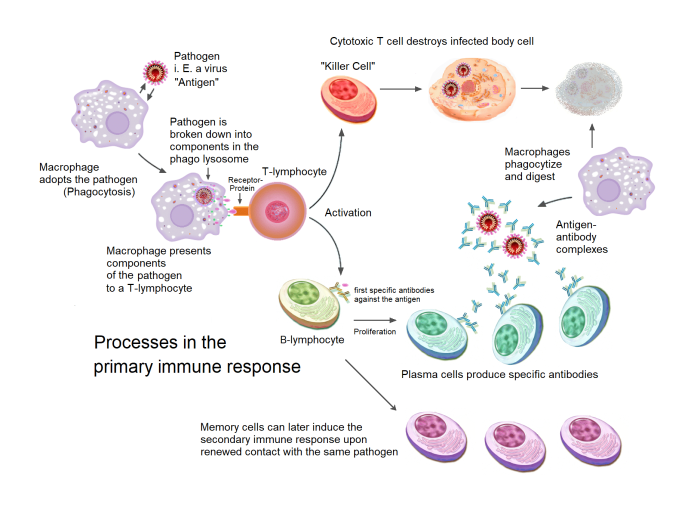
The absence of an immune response has profound clinical implications. It can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, impaired healing, and a higher risk of developing autoimmune diseases.The absence of an immune response can affect diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of diseases.
For example, in patients with impaired immune function, infections may be difficult to diagnose because the typical signs and symptoms of infection, such as fever and inflammation, may be absent. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, which can worsen the prognosis of the infection.Immune
modulators are medications that can be used to enhance or suppress the immune response. In patients with impaired immune function, immune modulators can be used to stimulate the immune system and improve the body’s ability to fight infection. In patients with autoimmune diseases, immune modulators can be used to suppress the immune system and reduce the severity of the disease.
Increased susceptibility to infectionsThe absence of an immune response can lead to increased susceptibility to infections. This is because the immune system is responsible for protecting the body from foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. When the immune system is impaired, the body is less able to fight off infections, which can lead to serious illness or even death.
Impaired healingThe immune system also plays a role in healing. When the immune system is impaired, the body is less able to repair damaged tissue. This can lead to delayed healing or even chronic wounds. Autoimmune diseasesThe immune system is responsible for distinguishing between self and non-self.
When the immune system is impaired, it may attack the body’s own tissues, leading to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases can affect any organ or tissue in the body, and they can be debilitating or even life-threatening.
Research and Future Directions

The absence of an immune response remains an intriguing and complex phenomenon with significant implications for understanding immune function. Current research is actively exploring the mechanisms and consequences of impaired immune response, with a focus on identifying potential therapeutic interventions.
One promising area of research involves the investigation of novel immune modulators. By targeting specific immune pathways or cells, researchers aim to enhance or restore immune function in individuals with impaired immune responses. This approach holds promise for treating a wide range of conditions, including infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
Genetic and Epigenetic Influences
Emerging research also explores the role of genetic and epigenetic factors in the absence of immune response. Identifying genetic variants and epigenetic modifications associated with impaired immune function can lead to personalized therapies tailored to individual patient profiles.
Immunosenescence and Aging, Absence results in no immune response
The age-related decline in immune function, known as immunosenescence, is another area of active research. Understanding the mechanisms underlying immunosenescence could pave the way for interventions to preserve immune function and reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
Potential Applications
The research on the absence of immune response has far-reaching implications for developing new therapies and treatments. By gaining a deeper understanding of the mechanisms involved, researchers can design targeted interventions to:
- Enhance immune responses in individuals with impaired immunity
- Prevent or treat autoimmune disorders by modulating immune responses
- Develop novel cancer immunotherapies to stimulate anti-tumor immune responses
Detailed FAQs: Absence Results In No Immune Response
What are the different types of immune responses?
There are two main types: innate immunity, which provides immediate but non-specific defense, and adaptive immunity, which develops over time and targets specific pathogens.
What is the role of antigens in immune response?
Antigens are molecules that trigger an immune response. They are recognized by immune cells, which then initiate a cascade of events to neutralize the foreign substance.
What are the consequences of impaired immune function?
Impaired immune function can lead to increased susceptibility to infections and diseases, as well as chronic conditions such as autoimmune disorders and cancer.