Joints and movement worksheet answers provide a comprehensive understanding of the human body’s intricate musculoskeletal system. This guide delves into the various types of joints, their structure, function, and their role in facilitating movement. It also explores common joint injuries, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, empowering readers with the knowledge to maintain optimal joint health.
Understanding the mechanics of joints is essential for maximizing physical performance, preventing injuries, and maintaining overall well-being. This guide serves as a valuable resource for students, fitness professionals, healthcare practitioners, and anyone seeking to enhance their knowledge of human movement and joint function.
Joint Structure and Function
Joints are the points of connection between two or more bones in the body. They allow for movement, provide support, and protect the bones from damage.
There are three main types of joints in the human body:
- Synarthrosesare immovable joints, such as the joints between the bones of the skull.
- Amphiarthrosesare slightly movable joints, such as the joints between the vertebrae.
- Diarthrosesare freely movable joints, such as the knee joint.
Each type of joint has a different structure and function.
Synarthroses
Synarthroses are immovable joints that are held together by connective tissue. They allow for no movement between the bones.
There are three types of synarthroses:
- Suturesare found between the bones of the skull. They are held together by dense connective tissue.
- Syndesmosesare found between the bones of the forearm and leg. They are held together by ligaments.
- Gomphosesare found between the teeth and the jawbone. They are held together by the periodontal ligament.
Amphiarthroses
Amphiarthroses are slightly movable joints that are held together by cartilage. They allow for a small amount of movement between the bones.
There are two types of amphiarthroses:
- Cartilaginous jointsare found between the vertebrae. They are held together by intervertebral discs.
- Symphysesare found between the pubic bones. They are held together by fibrocartilage.
Diarthroses
Diarthroses are freely movable joints that are held together by a joint capsule. They allow for a wide range of movement between the bones.
There are six types of diarthroses:
- Ball-and-socket jointsare found in the shoulder and hip. They allow for a wide range of movement, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
- Hinge jointsare found in the elbow and knee. They allow for flexion and extension.
- Pivot jointsare found in the neck and wrist. They allow for rotation.
- Gliding jointsare found in the wrist and ankle. They allow for gliding movements.
- Condyloid jointsare found in the wrist and fingers. They allow for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction.
- Saddle jointsare found in the thumb. They allow for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and opposition.
Joint Movements
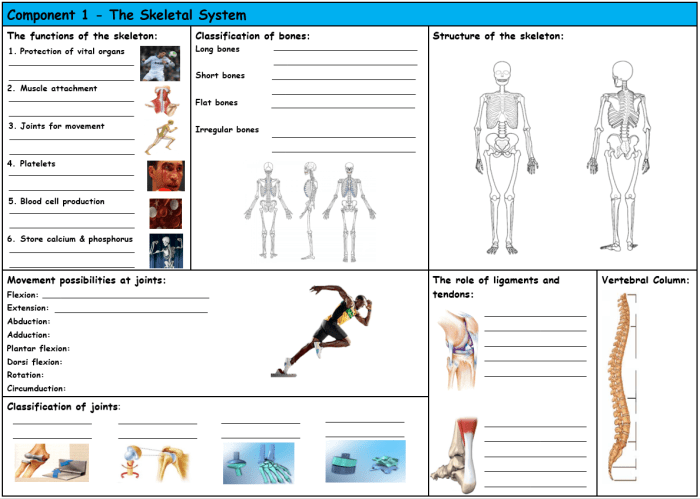
Joint movements are essential for a wide range of activities, from walking and running to playing sports and performing daily tasks. Understanding the different types of joint movements and the muscles and bones involved can help you improve your range of motion, prevent injuries, and enhance your overall physical performance.
Joint movements are classified into two main categories: angular movements and gliding movements.
Angular Movements
Angular movements involve rotation around an axis. There are three main types of angular movements:
- Flexion: Decreases the angle between two bones. For example, bending your elbow.
- Extension: Increases the angle between two bones. For example, straightening your knee.
- Rotation: Movement around a longitudinal axis. For example, turning your head from side to side.
Gliding Movements
Gliding movements involve sliding of one bone surface against another. There are two main types of gliding movements:
- Translation: Movement in a straight line, parallel to the surface of the joint. For example, moving your fingers side to side.
- Circumduction: Movement in a circular path. For example, swinging your arm in a circle.
Each type of joint movement is performed by specific muscles and bones. For example, flexion of the elbow is performed by the biceps muscle, while extension of the knee is performed by the quadriceps muscle.
Improving Range of Motion
Regular exercise can help improve your range of motion in different joints. Some examples of exercises that can improve range of motion include:
- Stretching: Stretching exercises can help to increase the flexibility of the muscles and connective tissues around the joints.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises can help to improve the strength of the muscles that control the joints.
- Range of motion exercises: Range of motion exercises are designed to improve the range of motion in specific joints.
Joint Injuries: Joints And Movement Worksheet Answers
Joint injuries are a common occurrence, affecting people of all ages and activity levels. They can range from minor sprains and strains to more serious injuries, such as dislocations and fractures. Joint injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, overuse, and underlying medical conditions.
The most common types of joint injuries include:
- Sprains:Sprains are injuries to the ligaments, which are the tough bands of tissue that connect bones together. Sprains can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the ligament damage.
- Strains:Strains are injuries to the muscles or tendons, which are the tough bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones. Strains can also range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the muscle or tendon damage.
- Dislocations:Dislocations occur when a bone is forced out of its normal position in a joint. Dislocations can be very painful and can cause significant damage to the joint.
- Fractures:Fractures are breaks in the bones. Fractures can occur in any bone in the body, including the bones in the joints. Fractures can be caused by trauma, such as a fall or a car accident, or by overuse, such as running or jumping.
The symptoms of a joint injury can vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. However, some common symptoms include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Stiffness
- Loss of range of motion
The treatment for a joint injury will also vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. However, some common treatment options include:
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
- Pain relievers
- Physical therapy
There are a number of things you can do to help prevent joint injuries, including:
- Warm up before exercising.
- Cool down after exercising.
- Stretch regularly.
- Wear proper footwear.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking.
- Eat a healthy diet.
Joint Health
Maintaining healthy joints is crucial for overall mobility, flexibility, and well-being. Joints are complex structures that connect bones, allowing for movement and providing support. When joints are healthy, they function smoothly, enabling us to perform daily activities without pain or discomfort.Regular
exercise is vital for joint health. It strengthens the muscles surrounding the joints, providing stability and reducing stress on the joint structures. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, or strength training, help build bone density and improve joint function. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, are also beneficial as they minimize stress on the joints while still promoting movement.Nutrition
plays a significant role in joint health. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients that support joint health. Calcium and vitamin D are crucial for bone health, while omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce joint pain and stiffness.
Maintaining a healthy weight can also reduce stress on the joints, especially weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.Lifestyle factors can also impact joint health. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can damage joint tissues and increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can help protect joint health. Additionally, getting enough sleep allows the body to repair and restore joint tissues.By incorporating regular exercise, a healthy diet, and positive lifestyle habits, we can improve joint health and reduce the risk of joint problems.
This includes managing weight, maintaining good posture, and using proper techniques when lifting heavy objects. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help monitor joint health and address any concerns early on.
Joint Assessment and Evaluation

Joint assessment and evaluation are crucial for diagnosing and managing joint disorders. It involves a comprehensive examination of the joint’s structure, function, and range of motion.
Methods of Joint Assessment
Various methods are employed to assess joint function:
- Inspection:Visual examination of the joint for swelling, deformity, or discoloration.
- Palpation:Feeling the joint for tenderness, warmth, or crepitus (grinding sensation).
- Range of Motion (ROM):Measuring the joint’s ability to move through its full range of motion.
- Special Tests:Specific maneuvers performed to assess ligamentous or capsular integrity.
- Imaging:X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to visualize joint structures and identify any abnormalities.
Interpretation of Results
The results of joint assessments are interpreted based on the patient’s history, physical examination findings, and imaging studies.
- Pain and Tenderness:Indicate inflammation, tissue damage, or nerve irritation.
- Swelling:Suggests fluid accumulation due to injury, infection, or arthritis.
- Deformity:May indicate dislocation, fracture, or chronic joint disease.
- Limited ROM:Can result from pain, stiffness, muscle weakness, or joint instability.
- Crepitus:Often associated with osteoarthritis or other degenerative joint conditions.
Guidelines for Joint Health Evaluation
Regular joint health evaluations are essential for early detection and management of potential problems.
- Assess for Pain:Joint pain that persists or worsens should be evaluated.
- Monitor Swelling:Persistent or recurring swelling can indicate underlying joint pathology.
- Check for Deformity:Any visible joint deformity warrants further investigation.
- Evaluate ROM:Limited or painful joint movement should be assessed.
- Consider Age and Occupation:Individuals with physically demanding occupations or those over the age of 50 are at higher risk for joint problems.
Joint Interventions and Treatment
Joint problems can range from minor sprains and strains to more serious conditions like arthritis. The type of treatment will depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause.
Conservative Treatment, Joints and movement worksheet answers
- Rest:Resting the affected joint can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Ice:Applying ice to the affected joint can help to reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression:Wrapping the affected joint with an elastic bandage can help to reduce swelling and provide support.
- Elevation:Elevating the affected joint above the level of the heart can help to reduce swelling.
- Physical therapy:Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility in the affected joint.
Medical Treatment
- Pain medication:Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain.
- Anti-inflammatory medication:Prescription anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids, can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs):DMARDs are medications that can help to slow the progression of certain types of arthritis.
- Biologic response modifiers (BRMs):BRMs are medications that can help to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Treatment
- Arthroscopy:Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that can be used to diagnose and treat joint problems.
- Joint replacement:Joint replacement is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged joint with an artificial joint.
Selecting the Appropriate Treatment
The type of treatment that is most appropriate for a particular joint condition will depend on the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and the patient’s individual needs. In general, conservative treatment is recommended for mild to moderate joint problems.
Medical treatment may be necessary for more severe joint problems or for conditions that do not respond to conservative treatment. Surgical treatment is typically reserved for severe joint problems that cannot be treated with conservative or medical treatment.
Top FAQs
What are the different types of joints in the human body?
There are six main types of joints in the human body: synovial, cartilaginous, fibrous, saddle, pivot, and ball-and-socket.
What is the function of synovial joints?
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body. They allow for a wide range of movement, including flexion, extension, rotation, and circumduction.
What are the symptoms of a joint injury?
Common symptoms of a joint injury include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the joint.
How can I prevent joint injuries?
There are several ways to prevent joint injuries, including warming up before exercise, stretching regularly, and using proper technique when lifting weights.