Renaissance and reformation pdf answer key – Unveiling the intricacies of the Renaissance and Reformation periods, this comprehensive guide offers a profound understanding of their transformative impact on history, culture, and society. From the dawn of humanism to the rise of Protestantism and scientific advancements, this PDF answer key provides an immersive journey into one of the most pivotal eras in human civilization.
Delving into the historical context, key figures, and lasting legacy of these movements, this resource equips readers with a thorough grasp of the factors that shaped the modern world. Through engaging narratives and insightful analysis, this guide illuminates the complexities of the Renaissance and Reformation, leaving an enduring impression on the minds of learners.
Renaissance and Reformation Overview
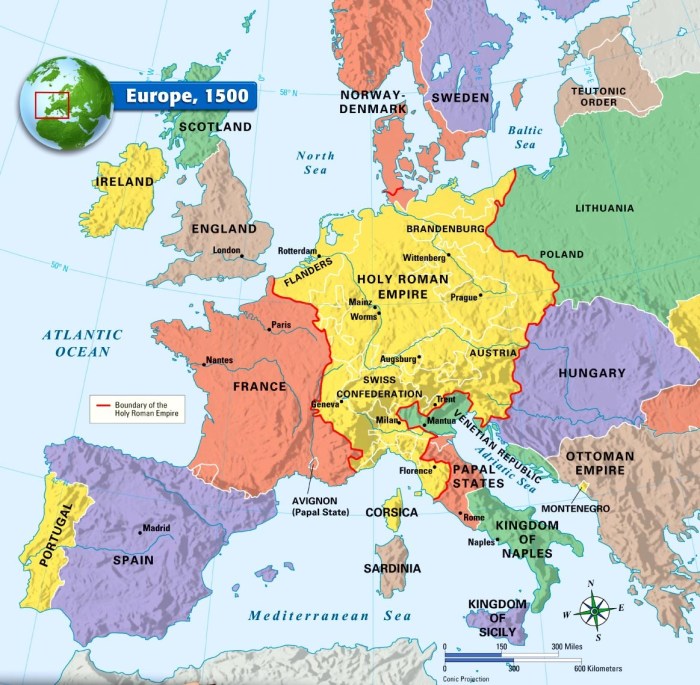
The Renaissance and Reformation were transformative periods in European history, marked by profound intellectual, cultural, and religious changes. The Renaissance, beginning in the 14th century, witnessed a renewed interest in classical learning and humanism, while the Reformation, starting in the 16th century, challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and led to the rise of Protestantism.
Timeline of Key Events:
- 14th century: Beginning of the Renaissance in Italy
- 1517: Martin Luther posts the Ninety-Five Theses
- 1520: Henry VIII breaks with the Catholic Church
- 1545-1563: Council of Trent
- 1648: Peace of Westphalia ends the Thirty Years’ War
Causes of the Renaissance:
- Growth of trade and commerce
- Increased availability of classical texts
- Patronage of wealthy individuals and city-states
Consequences of the Renaissance:
- Emergence of humanism and rationalism
- Artistic and scientific advancements
- Spread of new ideas through printing
Causes of the Reformation:
- Criticism of Catholic Church practices
- Rise of individualism and literacy
- Political and economic factors
Consequences of the Reformation:
- Religious division in Europe
- Political and social upheaval
- Spread of Protestantism and religious pluralism
Humanism and Rationalism
The Renaissance witnessed a renewed emphasis on human reason and the study of classical texts. Humanism, a philosophical movement, emphasized the importance of human potential, individuality, and the pursuit of knowledge. Rationalism, a methodological approach, promoted the use of reason and logic to understand the world.
Impact of Humanism on Education and Literature:
- Establishment of new universities
- Emphasis on classical languages and literature
- Development of new educational methods
Impact of Rationalism on Scientific Advancements and the Arts:
- Emphasis on observation and experimentation
- Development of new scientific theories
- Exploration of perspective and realism in art
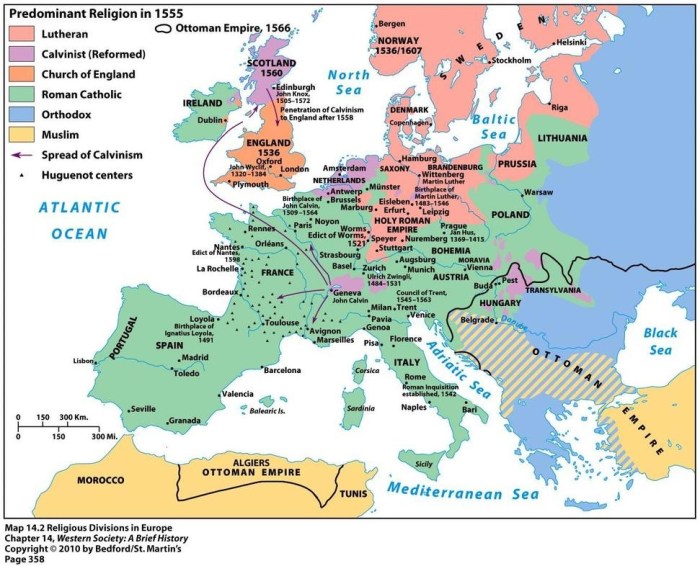
Religious Reform
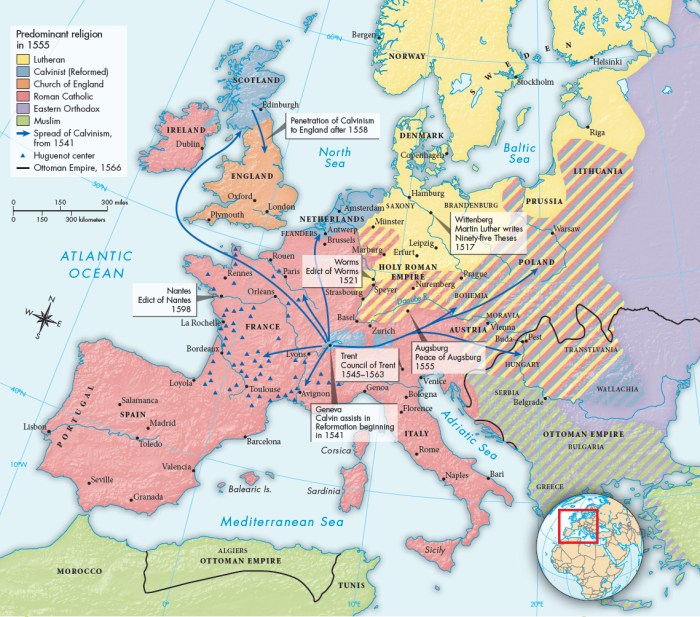
The Protestant Reformation, sparked by Martin Luther’s criticism of the Catholic Church, led to the rise of Protestantism and a fundamental shift in the religious landscape of Europe. Key figures included Martin Luther, John Calvin, and Henry VIII.
Key Ideas of the Protestant Reformation:
- Justification by faith alone
- Sola Scriptura (reliance on the Bible as the sole source of religious authority)
- Priesthood of all believers
Impact of the Reformation on Religious and Political Landscapes:
- Division of Europe into Catholic and Protestant regions
- Political and religious conflicts, including the Thirty Years’ War
- Spread of Protestantism beyond Europe
Art and Architecture
The Renaissance witnessed a revival of classical ideals and a renewed focus on humanism in art and architecture. Renaissance artists sought to portray the human form realistically and explore perspective and realism.
Characteristics of Renaissance Art and Architecture:
- Emphasis on human anatomy and perspective
- Use of classical motifs and architectural elements
- Patronage of wealthy individuals and city-states
Famous Works and Artists:
- Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci
- Sistine Chapel ceiling by Michelangelo
- St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome
Science and Exploration
The Renaissance and Reformation were periods of significant scientific advancements and geographical discoveries. Scholars such as Copernicus, Galileo, and Vesalius made groundbreaking contributions to astronomy, physics, and anatomy.
Scientific Advancements:
- Copernicus’ heliocentric model of the solar system
- Galileo’s discoveries in astronomy
- Vesalius’ groundbreaking work in anatomy
Exploration:
- Portuguese and Spanish voyages to the Americas
- Exploration of new trade routes to Asia
- Expansion of European empires
Impact on Modern Society: Renaissance And Reformation Pdf Answer Key
The Renaissance and Reformation had a profound impact on the development of modern society. Their legacy can be seen in education, religion, the arts, and political thought.
Impact on Education:
- Establishment of modern universities
- Emphasis on classical and humanistic education
- Spread of literacy and knowledge
Impact on Religion:
- Rise of Protestantism and religious pluralism
- Separation of church and state in some societies
- Continued influence of religious ideas on society
Impact on the Arts:
- Development of modern artistic techniques
- Influence of classical and humanistic ideals
- Emergence of new art forms, such as opera
Q&A
What were the key causes of the Renaissance?
The Renaissance was sparked by a confluence of factors, including the rediscovery of classical texts, the rise of humanism, and the growth of trade and commerce.
Who were the key figures of the Reformation?
Martin Luther, John Calvin, and Henry VIII were central figures in the Protestant Reformation, leading movements that challenged the authority of the Catholic Church.
What were the major scientific advancements of the Renaissance and Reformation?
The Renaissance and Reformation witnessed groundbreaking scientific discoveries by figures like Copernicus, Galileo, and Vesalius, laying the groundwork for the Scientific Revolution.