Embark on an intellectual journey into the intricate realm of court system and structure crossword answers, where the interplay of law and logic unravels the mysteries of the judicial process. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the hierarchy of courts, the roles of courtroom personnel, and the intricacies of court procedures, empowering you to navigate the legal landscape with confidence.
Delve into the fascinating world of courtrooms, where judges preside over proceedings, attorneys present their cases, and juries weigh evidence to determine the truth. Understand the nuances of courtroom etiquette and the importance of access to justice, ensuring that all individuals have a fair and equitable opportunity to seek legal recourse.
Court System Structure
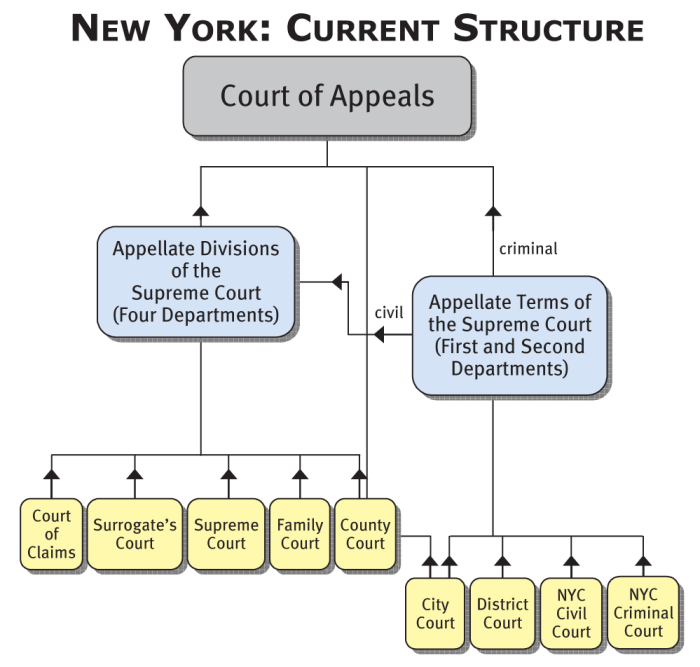
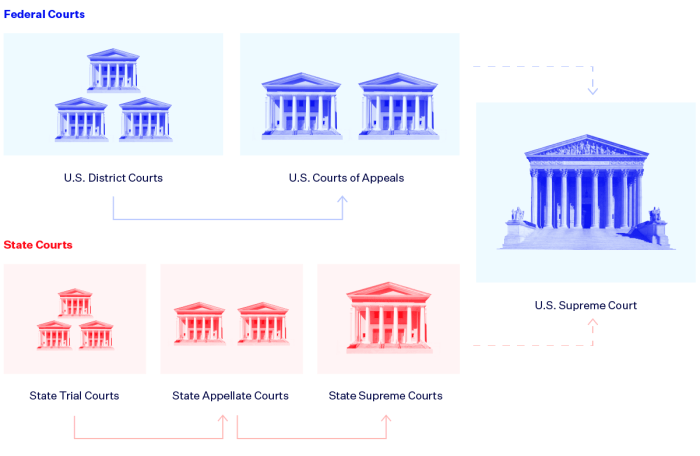
The court system in the United States is a complex and hierarchical structure, with different levels of courts having different jurisdictions and responsibilities. The hierarchy of courts is typically as follows:
- Supreme Court:The highest court in the land, the Supreme Court has the power to review decisions made by lower courts and to interpret the Constitution.
- Federal Appellate Courts:There are 13 federal appellate courts, which review decisions made by federal district courts.
- Federal District Courts:There are 94 federal district courts, which hear most federal cases.
- State Supreme Courts:The highest court in each state, the state supreme court has the power to review decisions made by lower state courts.
- State Appellate Courts:There are intermediate appellate courts in many states, which review decisions made by lower state courts.
- State Trial Courts:There are various types of state trial courts, which hear most state cases.
The jurisdiction of a court refers to the types of cases that it can hear. For example, federal courts have jurisdiction over cases involving federal law, while state courts have jurisdiction over cases involving state law.Appellate courts play a vital role in the court system by reviewing decisions made by lower courts.
They can uphold the lower court’s decision, reverse it, or send it back for further proceedings. Appellate courts also help to develop the law by interpreting statutes and issuing precedents that lower courts must follow.
Courtroom Personnel
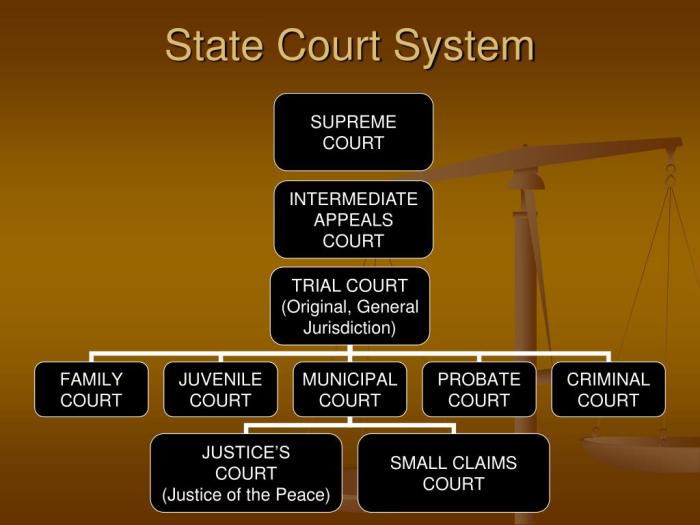
A courtroom proceeding typically involves several key personnel, each with specific roles and responsibilities:
- Judge:The judge presides over the courtroom and is responsible for ensuring that the proceedings are conducted fairly and in accordance with the law.
- Attorneys:Attorneys represent the parties involved in the case and present their arguments to the judge or jury.
- Jurors:Jurors are citizens who are selected to hear the evidence and decide the outcome of a trial.
The process of jury selection is designed to ensure that the jury is impartial and representative of the community. Jurors are typically selected from a pool of potential jurors who have been summoned to court. The attorneys for each side then question the potential jurors to determine if they have any biases or conflicts of interest that would prevent them from serving on the jury.The
jury plays a vital role in the court system by deciding the facts of the case and reaching a verdict. In most cases, the jury’s verdict is final and binding on the parties involved.
Court Procedures
A typical court case involves several steps, from filing a complaint to issuing a judgment:
- Filing a Complaint:The plaintiff files a complaint with the court, which Artikels the legal claims against the defendant.
- Service of Process:The defendant is served with a copy of the complaint and a summons, which informs them of the lawsuit and requires them to respond.
- Discovery:The parties exchange information and documents relevant to the case.
- Motions:The parties may file motions with the court to request specific actions, such as dismissing the case or compelling the other party to produce evidence.
- Trial:If the case cannot be resolved through settlement or summary judgment, it will proceed to trial. The trial involves the presentation of evidence, the examination of witnesses, and the arguments of the attorneys.
- Verdict:The jury or judge reaches a verdict, which decides the outcome of the case.
- Judgment:The court issues a judgment, which is the final and binding decision in the case.
Motions are formal requests made to the court by the parties involved in a case. Motions can be used to request a variety of different actions, such as dismissing the case, compelling the other party to produce evidence, or changing the venue of the trial.
The court will consider the arguments of the parties and issue a ruling on the motion.Discovery is the process of exchanging information and documents relevant to the case. Discovery helps to ensure that both parties have all of the information they need to prepare for trial.
Discovery can include interrogatories, requests for production of documents, and depositions.
Courtroom Etiquette: Court System And Structure Crossword Answers
Courtroom etiquette refers to the expected behavior and conduct in a courtroom. It is important to maintain proper courtroom etiquette to ensure that the proceedings are conducted fairly and respectfully.Some basic rules of courtroom etiquette include:
- Be on time for all court appearances.
- Dress appropriately.
- Be respectful to the judge, attorneys, and other court personnel.
- Do not speak unless you are called upon to do so.
- Do not use cell phones or other electronic devices in the courtroom.
- Do not chew gum or eat food in the courtroom.
Violating courtroom etiquette can have consequences, such as being removed from the courtroom or even being held in contempt of court.
Access to Justice
Access to justice refers to the ability of individuals to obtain fair and equal treatment in the court system. Access to justice is essential for a just and equitable society.There are a number of challenges that individuals may face in seeking access to justice, including:
- Financial barriers:Legal fees can be expensive, which can make it difficult for low-income individuals to afford legal representation.
- Language barriers:Individuals who do not speak English may have difficulty understanding the legal process and obtaining legal assistance.
- Cultural barriers:Cultural norms and beliefs can affect an individual’s ability to access the court system.
There are a number of programs and initiatives aimed at improving access to justice for all individuals. These programs include:
- Legal aid organizations:Legal aid organizations provide free or low-cost legal assistance to low-income individuals.
- Pro bono programs:Pro bono programs allow attorneys to volunteer their time to represent low-income individuals.
- Language access programs:Language access programs provide interpretation and translation services to individuals who do not speak English.
Improving access to justice is an ongoing challenge, but it is essential for ensuring that all individuals have the opportunity to obtain fair and equal treatment in the court system.
FAQ
What is the hierarchy of courts in the United States?
The federal court system consists of three levels: district courts, circuit courts of appeals, and the Supreme Court. Each state also has its own court system, typically with trial courts, intermediate appellate courts, and a state supreme court.
What are the different types of courts?
There are many different types of courts, including criminal courts, civil courts, family courts, and juvenile courts. Each type of court has specific jurisdiction over certain types of cases.
What is the role of appellate courts?
Appellate courts review decisions made by lower courts. They can uphold the lower court’s decision, reverse it, or send it back for further proceedings.