Which of the genotypes in #1 would be considered purebred – Exploring which genotypes in #1 are considered purebred, this discussion delves into the fundamentals of genetics and the characteristics that define purebred genotypes. Understanding the distinction between purebred and non-purebred genotypes is crucial in various fields, including animal breeding and genetic research.
The following sections will delve into the concepts of homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, explain the criteria for identifying purebred genotypes, and provide examples to illustrate these principles. Additionally, we will discuss methods for determining genotype purity and explore the significance of purebred genotypes in different contexts.
Genotype Definitions: Which Of The Genotypes In #1 Would Be Considered Purebred
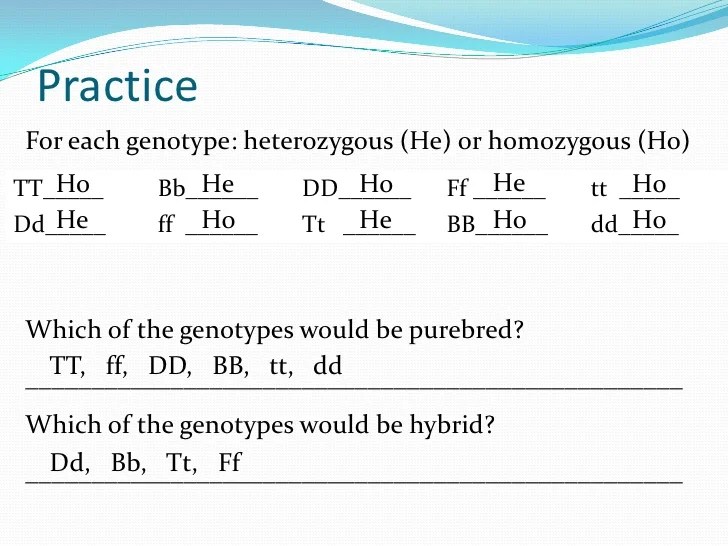
A genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, comprising the alleles present at specific gene loci. It determines the organism’s genetic traits, which are the observable characteristics that result from gene expression. Purebred genotypes are those in which both alleles at a given gene locus are identical, resulting in the expression of a single trait.
Homozygous vs. Heterozygous Genotypes
Homozygous genotypes have identical alleles at a specific gene locus, resulting in the expression of a single trait. Heterozygous genotypes, on the other hand, have different alleles at the same gene locus, leading to the expression of both traits associated with those alleles.
Examples:
- Homozygous dominant (AA): Expresses only the dominant trait
- Homozygous recessive (aa): Expresses only the recessive trait
- Heterozygous (Aa): Expresses both dominant and recessive traits
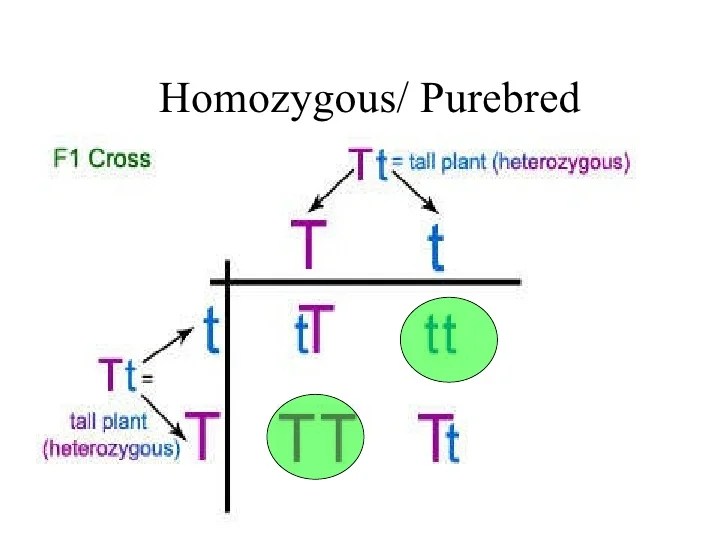
Identifying Purebred Genotypes
Purebred genotypes are characterized by the expression of a single trait, as both alleles at a specific gene locus are identical. To determine if a genotype is purebred, one must observe the organism’s phenotype (observable traits) and determine if it expresses a single trait.
Additionally, genetic testing can be used to confirm the presence of identical alleles at a given gene locus.
Genotype Table Analysis
| Genotype | Phenotype | Purebred |
|---|---|---|
| AA | Dominant trait | Yes |
| Aa | Both dominant and recessive traits | No |
| aa | Recessive trait | Yes |
Examples of Purebred Genotypes

Black fur in dogs:The dominant allele (B) codes for black fur, while the recessive allele (b) codes for brown fur. A homozygous dominant genotype (BB) will result in a purebred black dog, expressing only the black fur trait.
Blue eyes in humans:The recessive allele (b) codes for blue eyes, while the dominant allele (B) codes for brown eyes. A homozygous recessive genotype (bb) will result in a purebred individual with blue eyes, expressing only the blue eye trait.
Methods for Determining Genotype Purity
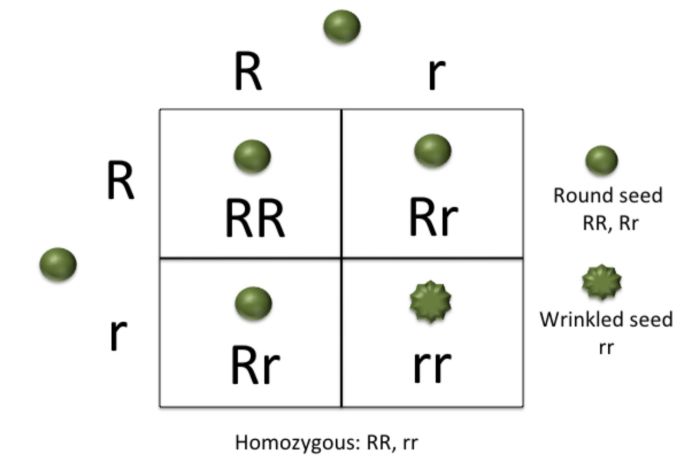
Pedigree analysis:This method involves examining the genetic history of an organism to identify patterns of inheritance that suggest purebred genotypes.
Genetic testing:This method involves analyzing the DNA of an organism to determine the presence of identical alleles at specific gene loci.
Phenotypic observation:This method involves observing the organism’s phenotype and determining if it expresses a single trait, which may indicate a purebred genotype.
Question Bank
What is a purebred genotype?
A purebred genotype is one in which both alleles for a particular gene are identical, resulting in a homozygous condition.
How can you determine if a genotype is purebred?
To determine if a genotype is purebred, examine the alleles for a specific gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is purebred (homozygous).
What is the difference between a homozygous and a heterozygous genotype?
A homozygous genotype has two identical alleles for a gene, while a heterozygous genotype has two different alleles for a gene.