Ana titer 1 1280 homogeneous – Delving into the world of ANA titer 1:1280 homogeneous, we embark on a journey to unravel its clinical implications and associated autoimmune diseases. This unique antibody pattern holds valuable insights into our immune system’s complexities, guiding us towards accurate diagnoses and effective patient management.
ANA testing plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases, and a titer of 1:1280 with a homogeneous pattern warrants further investigation. Understanding its significance empowers us to provide timely and appropriate care, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Definition and Background
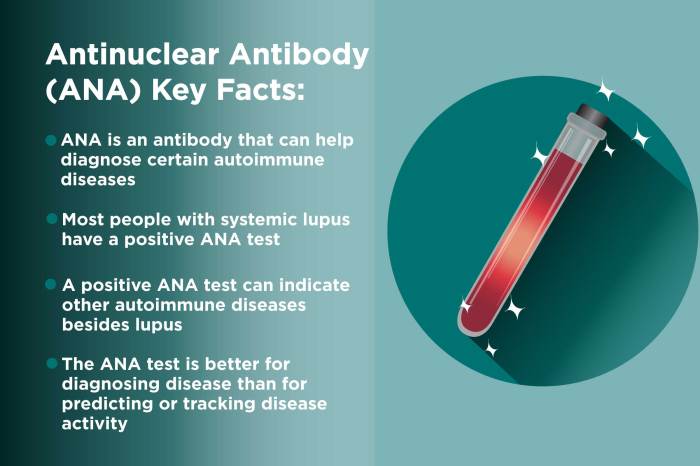
An ANA titer test measures the level of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in your blood. ANA are antibodies that attack your body’s own cells, specifically the nucleus of the cells. A high ANA titer can indicate an autoimmune disease, in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your own tissues.
Types of ANA Patterns
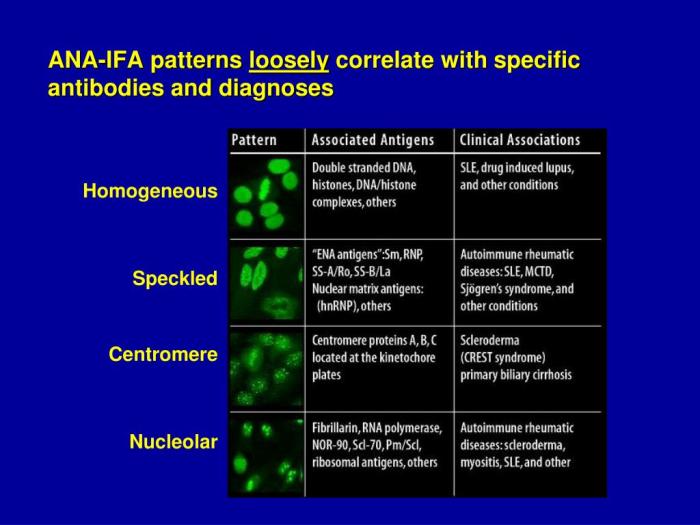
There are many different types of ANA patterns, each of which can be associated with a specific autoimmune disease. Some of the most common ANA patterns include:
- Homogeneous pattern:This pattern is seen in people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
- Speckled pattern:This pattern is seen in people with Sjögren’s syndrome and mixed connective tissue disease.
- Nucleolar pattern:This pattern is seen in people with scleroderma.
- Centromere pattern:This pattern is seen in people with CREST syndrome.
Role of ANA Testing in Diagnosing Autoimmune Diseases
ANA testing is a helpful tool for diagnosing autoimmune diseases. However, it is important to note that a positive ANA test does not always mean that you have an autoimmune disease. Many people with autoimmune diseases have a negative ANA test, and many people with a positive ANA test do not have an autoimmune disease.
If you have a positive ANA test, your doctor will likely order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis of an autoimmune disease. These tests may include blood tests, imaging tests, and biopsies.
Understanding the significance of ana titer 1 1280 homogeneous is crucial for aspiring healthcare professionals. If you’re looking to enhance your knowledge, check out the unit 2 aphg practice test for a comprehensive review of key concepts. By delving into this practice test, you can solidify your understanding of ana titer 1 1280 homogeneous and other essential topics.
Interpretation of ANA Titer 1
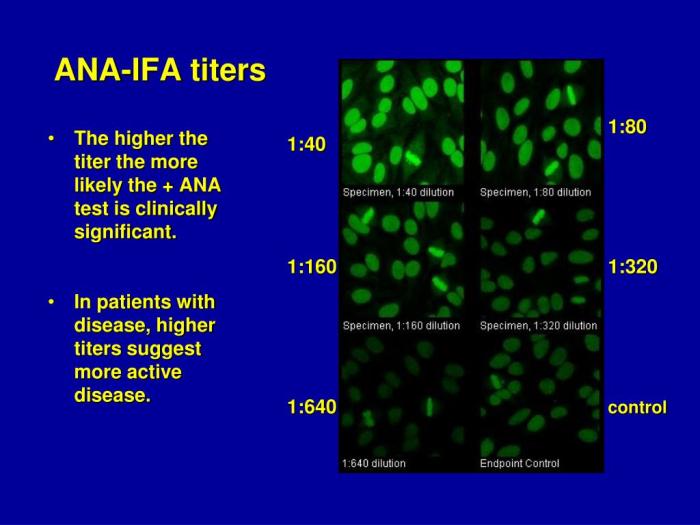
An ANA titer of 1:1280 with a homogeneous pattern is considered a high-titer result. A homogeneous pattern means that the ANA antibodies are evenly distributed throughout the cell nucleus.
This specific result may indicate the presence of an underlying autoimmune disorder, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, or Sjogren’s syndrome.
Differential Diagnoses
The differential diagnoses associated with a high-titer homogeneous ANA pattern include:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- Mixed connective tissue disease
- Drug-induced lupus
Associated Autoimmune Diseases
An ANA titer of 1:1280 homogeneous is strongly associated with autoimmune diseases. These diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues.
The most common autoimmune diseases associated with this ANA titer include:
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Clinical Manifestations:SLE can affect multiple organs, causing symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and kidney problems.
- Diagnostic Criteria:The diagnosis of SLE is based on a combination of clinical symptoms and laboratory tests, including the presence of specific autoantibodies and a positive ANA titer.
- Treatment Options:Treatment for SLE typically involves medications to suppress the immune system and manage symptoms.
Sjögren’s Syndrome
- Clinical Manifestations:Sjögren’s syndrome affects the exocrine glands, leading to dryness of the eyes and mouth. Other symptoms may include joint pain, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Diagnostic Criteria:Diagnosis involves a combination of symptoms, a positive ANA titer, and the presence of specific autoantibodies.
- Treatment Options:Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications, such as using artificial tears for dry eyes and medications to reduce inflammation.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Clinical Manifestations:RA primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. It can also lead to fatigue, weight loss, and anemia.
- Diagnostic Criteria:Diagnosis is based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests, including a positive ANA titer and the presence of specific autoantibodies.
- Treatment Options:Treatment aims to reduce inflammation and pain, prevent joint damage, and improve function. It may involve medications, physical therapy, and surgery in severe cases.
Importance of Further Testing and Specialist Referral
An ANA titer of 1:1280 homogeneous indicates a high likelihood of an autoimmune disease. Further testing is necessary to determine the specific disease and assess the extent of involvement. Specialist referral to a rheumatologist is recommended for proper diagnosis, management, and treatment.
Differential Diagnoses
An ANA titer of 1:1280 homogeneous can be a sign of an underlying autoimmune disease, but it’s important to consider other potential causes as well.
Non-autoimmune conditions, infections, and medications can also lead to a positive ANA result. Ruling out these alternative diagnoses is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Non-Autoimmune Conditions
- Liver disease
- Chronic infections (e.g., hepatitis, Epstein-Barr virus)
- Certain cancers (e.g., lung cancer, breast cancer)
Infections
- Viral infections (e.g., parvovirus B19, HIV)
- Bacterial infections (e.g., syphilis, Lyme disease)
- Parasitic infections (e.g., malaria)
Medications
- Anticonvulsants (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine)
- Antibiotics (e.g., penicillin, sulfonamides)
- Antimalarial drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine)
Clinical Management and Monitoring
The clinical management of patients with an ANA titer of 1:1280 homogeneous depends on the underlying disease and the patient’s symptoms.
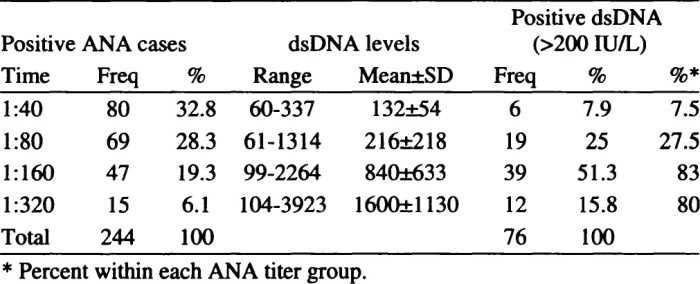
Monitoring the disease activity is important to assess the response to treatment and to detect any disease flare-ups. Serial ANA testing can be used to monitor disease activity, along with other laboratory investigations such as complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein.
Patient Education, Ana titer 1 1280 homogeneous
Patient education is crucial to empower patients to manage their condition effectively. Patients should be educated about their disease, the importance of medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing symptoms and improving overall health. Patients should be encouraged to:
- Get regular exercise
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Get enough sleep
- Manage stress
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Medication Management
Medication management is often necessary to control disease activity and prevent complications. The choice of medication will depend on the underlying disease and the patient’s individual needs.
- Immunosuppressants
- Biologic response modifiers
- Corticosteroids
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Commonly Asked Questions: Ana Titer 1 1280 Homogeneous
What is the significance of an ANA titer of 1:1280 homogeneous?
A titer of 1:1280 with a homogeneous pattern indicates a high level of antibodies targeting nuclear components, suggesting a strong immune response. It is commonly associated with autoimmune diseases, particularly systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
What are the most common autoimmune diseases associated with ANA titer 1:1280 homogeneous?
SLE is the most common autoimmune disease linked to this antibody pattern, followed by Sjogren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and mixed connective tissue disease.
What are the potential differential diagnoses for ANA titer 1:1280 homogeneous?
Infections, medications, and non-autoimmune conditions can also cause a positive ANA result. Ruling out these alternative diagnoses is crucial to ensure an accurate diagnosis.